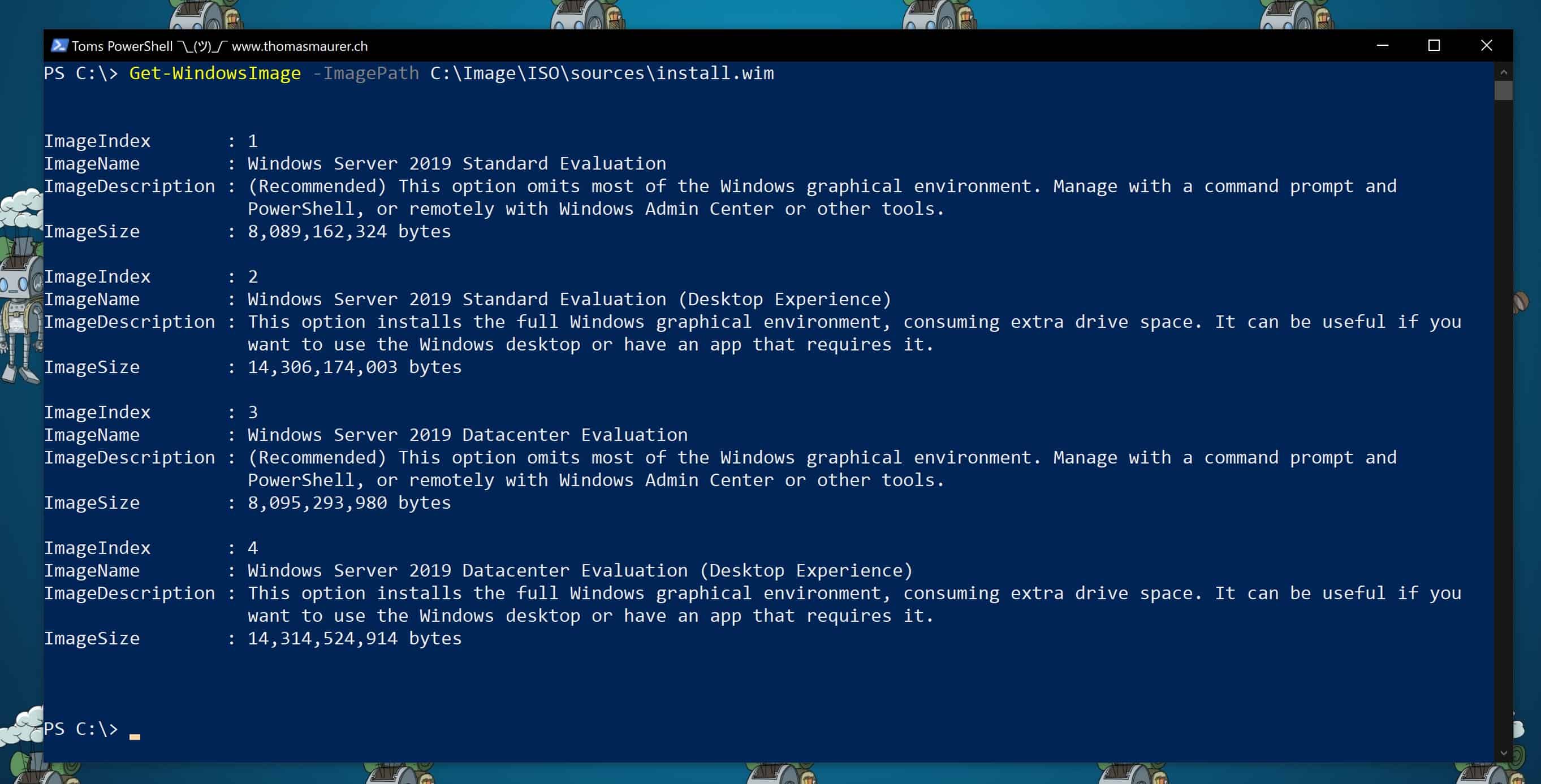
Look for the drive that is identified as the 3TB drive (2794GB). The properties window shows that the partition table on the drive is MBR. Important: note the Disk number (such as Disk 1). Open a Command Prompt window. To open the Command Prompt on a Windows Vista or Windows 7 machine click on Start and type cmd in the search bar. Hard drive,SSD and eMMC drives use it to measure whether it’s failing or not. There are many applications which come with Hard disks to generate SMART reports.There are also third party application for the same. In Windows 10 there are certain in-built tools which help to generate the Hard disk status as well as health. SYBA SI-PEX40062 PCI-Express 2.0 x2 Low Profile Ready SATA III (6.0Gb/s) Controller Card. Internal Connectors: 4 x SATA 6.0Gb/s Transfer Rate: Up to 6Gb/s Operating Systems Supported: Windows 8 Windows 7 Vista Windows XP Server 2008 Server 2008 R2 Server 2003 Linux 2.6.x and Above (AHCI devices driver is a built-in feature) Package Contents: SATA III 4-port PCI-e Version 2, x2 Slot Controller.
Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q.)
How to start using Hard Disk Sentinel?
No hard disk temperature/health displayed. What is wrong?
Why no disk information detected for my RAID array?
Why hard disk temperature is so important?
Which S.M.A.R.T. parameters are significant?
How Hard Disk Sentinel warns me if there is a problem?
What languages are supported?
I'm a system administrator. Is it possible to detect hard disk status of a remote computer?
Is it possible to monitor disk status WITHOUT administrator rights?
I can't see the hard disk status on my drive icons. What can I do?
I encountered problem with Hard Disk Sentinel. What can I do?
No Performance information displayed. What is wrong?
I have bad sectors and my disk health is 90%. Do I need to worry or ask for replacement drive?
Hard disk health is low or recently changed or I just installed a new (used) hard disk. How can I perform a deep analysis?
Why other software displays different health? Which is correct?
I believe TRIM is enabled (fsutil shows that), but Hard Disk Sentinel shows it is DISABLED. Why?
How to repair hard disk drive? How to eliminate displayed hard disk problems?
What is a weak sector? How to repair weak sectors?
Do you have other questions? Browse the Q&A Knowledge Base or just let us know!
No hard disk temperature/health displayed. What is wrong?
The question is: does the hard disk controller (and its driver) pass this command to the SSD(s) used in the system or block it? The problem is that some hard disk controllers (and their drivers) may block the TRIM command, do not pass it to the SSD, even if TRIM is supported by the SSD. (this is same as the 'Acoustic management' command for. Once loaded, click on the Hiren menu icon in the system tray and go to Registry - “Fix hard disk controller (fixhdc.cmd)”. Press the T key, then enter and type in the TargetRoot folder. The default would be C:Windows but might be different on multiboot systems, in which case you would need to check in Windows Explorer what the correct.
The problem is related to the actual hardware (hard disk controller, external enclosure, port multiplier, etc.) or its driver which may block the detection.
Updating the driver of the disk controller (if there is an updated version available) may help in this situation. If possible, you may try a different version of Windows because of the different driver sets.
This problem is more frequent if the hard disk controller driver is supplied during Windows installation (these drivers usually support only minimal features but not detecting details).
The issue is usually related to:
- AMD AHCI Compatible RAID controller: the driver of the current controller is old - and does not allow detection of hard disk status. Please find updated driver from the Driver Zone page. More information about Updating driver for AMD AHCI Compatible RAID Controller
- RAID arrays: most RAID controllers allow detection of hard disk status information when the hard disk drives are configured in RAID arrays. The list of such RAID controllers available in the 'RAID controllers' section at Hard Disk controllers. Other RAID controllers may prevent detection of hard disk information or provides only limited information.
- USB hard disks: most newer USB-ATA bridge chips used in USB hard disk enclosures supports the detection. Older chips (and early production of USB 3.0 chips, manufactured before Feb 2010) do not have the required function, that's why no hard disk information is displayed.
It is recommended to connect both ends of the Y USB cable when using 2.5' USB drives to supply enough power to the disk. - ITE controllers: these controllers usually provide disk information but only when non-RAID (ATA/ATAPI) firmware and driver set is used. This is available from the Driver Zone.
- VIA, JMicron JMB36X, Gigabyte GBB36X controllers: these controllers usually provide disk information but only with specific driver version. Please check the disk controller compatibility page for information about the recommended drivers.
- AHCI controllers: some AHCI controllers may not provide disk information. Disabling AHCI mode in BIOS setup can help in this situation.
- Older hard disks: they may do not support S.M.A.R.T. function which collects and reports the information to the software.
- Solid State Devices: most solid state devices provide health status but only few of them has temperature sensors. It is possible that SSDs provide limited information (for example no temperature and/or power on time value reported).
- Pendrives, memory cards: these devices appear as hard disks in Windows and in Hard Disk Sentinel. However, only very few of them provides any health, temperature information.
- IDE hard disks: make sure to not use 'cable select' jumper settings, just 'master' or 'slave' on the drives. (even if the hard disk is used in USB enclosure or with PATA/SATA converter). Use 80-wire standard cable (not round one) and the 'longer' end should be connected to the motherboard, the shorter end to the master device and the center connector to the slave device.
In such situations, please try the recommended solutions (try upgrading driver for the actual hard disk controller from the Driver Zone, firmware or using alternative USB enclosure if possible). You may use the Report menu Send test report to developer function to send a report about the current configuration and situation. Such reports help to analyze hardware information and verify why the information is not displayed and helps to improve the detection (if possible).
Alternatively, you may try the Hard Disk Sentinel for DOS (HDSDOS) tool, it may detect some information because under DOS there is no problematic Windows drivers loaded.
Please check the hardware compatibility page for more details. In the Driver Zone you may find better, recommended drivers for various controllers to monitor the status of connected hard disks/SSDs.
Anyway, the tests under Disk menu Surface Test function can be used to test and diagnose the hard disk, reveal and repair possible disk problems.
Why no disk information detected for my RAID array?
While Hard Disk Sentinel can communicate with most RAID controllers to detect hard disk status (health, temperature and all details), some RAID controllers simply do not have the required functions to access the hard disks behind the virtual drive available for use. In this situation the controller completely hides all physical disk information - that's why the real disk type and S.M.A.R.T. information (including temperature and health) are not displayed for hardware RAID arrays, regardless of the type (0, 1, etc...) of the array.
RAID controllers listed in the RAID controllers section on the compatible hard disk controllers page (for example 3ware / AMCC / Areca / HighPoint / LSI / Dell / NVIDIA / Silicon Image / Intel / JMicron / Adaptec / Promise Supertrak / IBM / VIA RAID controllers) have special methods - so with such RAID controllers it is possible to get hard disk status information. Some other controllers (for example ITE, Promise FastTrak, Ultra 320 SCSI RAID controllers) do not have this feature, that's why no information is displayed.
We do our best to examine other RAID controllers and support them, if possible - but some controllers simply do not allow this (due to the missing functions) and can't be supported by any software.
A possible solution is to use a completely OS controlled software RAID array. This way the disks provide full information without problems. It is officially possible by using 'Server' editions of Windows.
Anyway, the disk testing functions (Disk -> Surface test (both the read and write tests if applicable) and Random seek test) can be used on all storage volumes, including on such RAID arrays.
Why hard disk temperature is so important?
High speed hard disks, small and crowded chassis can cause very high temperatures. This means that the hard disk is not able to cool down. Disk performance and reliability significantly decrease as temperature increases and above 50 °C failure can occur any time. Disk manufacturers often limit the maximum operating temperature to 50 degree centigrade. However, it is recommended to keep your hard disks at lower temperature (approximately 35-40 °C is good) to increase their life time.
Which S.M.A.R.T. parameters are significant?
Not all hard disk support all such S.M.A.R.T. parameters, but here is the list of most significant values:
1 Raw Read Error Rate: Number of hardware read errors occurred when reading from the disk surface. Wrong surface or reading head condition may affect this value.
5 Reallocated Sectors Count: If the hard disk found an error, it tries to reallocate the data to a new, spare location and mark the original sector as reallocated to prevent further usage. This value is the number of such reallocated sectors.
7 Seek Error Rate: Errors found while the head(s) were seeking to a specific sector. This value indicates if there is a head positioning unit (servo) problem.
9 Power On Time: The number of minutes or hours (depends of the manufacturer of the disk) the drive is powered. This value is constantly increasing as 'total km' counter in cars.
10 Spin Retry Count: Hard disk could not spin up when the computer is powered and it needed to retry. Increasing this value is a possible sign of a faulty motor.
194 Disk Temperature: The temperature of the disk in °C units. Some models store different values for the disk and the electric board. Some models store not only current but maximum temperature reached also.
196 Reallocation Event Count: Number of reallocation operations started. This indicates both completed or failed reallocation operations.
197 Current Pending Sector Count: Number of 'weak' sectors waiting for reallocation. When the reallocation completed, this value may decrease.
198 Uncorrectable Sector Count: Number of uncorrectable errors. This is one of the most important values, it indicates the total number of unusable sectors. Increasing this value means that hard disk failure will be occurred.
200 Write Error Rate: Number of errors found during write operations to the disk surface.
These are the most important values. Some others indicate statistical information but some may be used for prediction of the hard disk status (for example, increasing hard disk spin up time or spin retry count may indicate problems as the hard disk can't start easily). For the complete list of parameters, please see the help.
How Hard Disk Sentinel warns me in case of a problem?
Without any special setting, the tray icon immediately reflects the problem by flashing a red X icon. Hard Disk Sentinel displays a tray icon bubble with the error and the hard disk. Optionally it is possible configure e-mail and/or network message alerts, sound warnings and the software can turn off the computer to prevent further degradation. The Professional version can also execute any external application or start a (backup) operation immediately, for example to backup data immediately from the failing drive to another.
The drive icons displayed in any application (for example, Windows Explorer) reflect the disk health status and free space of the drive.
If the small status window is visible, the error of the problematic hard disk is displayed there. You can check the details by inspecting the details and the full S.M.A.R.T. information table for the hard disk. The error is also logged into the log of the hard disk.
Bubble over the system tray icon showing the problem
The hard disk with problem is displayed also in small status window
What languages are supported?
Currently more than 25 different languages are supported (Bulgarian, Czech, English, Hungarian, Italian, French, Romanian, Russian, German, Chinese, Chinese (traditional), Spanish, Portuguese-Brazil, Dutch, Greek, etc.) languages are supported. To download the newest language files, please check the language support page or use the latest possible version which contains the most recent language files.
I'm a system administrator. Is it possible to detect hard disk status of a remote computer?
It is possible to configure Hard Disk Sentinel to send e-mail and/or network message if a failure predicted, if a hard disk is too hot or if a critical SMART parameter is degraded. Also it can be used to send daily reports about the current status of hard disks. So (under the licensing conditions) it is possible to install Hard Disk Sentinel on more computers and the computers report the problems to system administrator.
This requires the registered and activated version of Hard Disk Sentinel installed on the remote computer(s).
If you want to remotely monitor a single client, you can use the 'webstatus' feature of the software, to remotely log in by using any web browser.
For larger networks, Hard Disk Sentinel Enterprise Server, is the best solution which can manage many clients, display their details, logs and problems and issue alerts upon problem with any client.
Is it possible to monitor disk status WITHOUT administrator rights?
Yes, it is possible if Hard Disk Sentinel Professional runs as a service: then it can examine hard disk status even if there is no user logged to the computer or if the user does not have administrator rights (have limited rights only).
Generally in order to access the disk status, the software would require administrator user rights, this is why by default Hard Disk Sentinel needs to be run with administrator account.
It is possible to use the software differently: switch to NT Service mode after installation, by using Configuration -> Integration -> Use as service button. It switches Hard Disk Sentinel Professional to 'service' mode: then it runs in the context of the SYSTEM account, invisible in the background as an NT service and works independenty from the current user, without any visible user interface.

This way it can work (detect status, issue alerts by e-mail, report problems) independently from the current user and his user rights, so works even if the current user has limited user rights - or if there is no logged user at all. So in service mode, Hard Disk Sentinel Pro is separated from the current user.
When running in service mode, the current user (with limited rights) can start a 'Hard Disk Sentinel Tray' extension: with it, the user can get status information and tray icons showing the actual hard disk temperature, but without the opportunity to change options, configuration or perform tests etc. The idea is to let administrator use all functions/features - and if there is an user with limited user rights, he can still check status, but should have no rights to perform any special actions.
Please check https://www.hdsentinel.com/help/en/330_c_integration.html for more details about the service mode in general.
I can't see the hard disk status on my drive icons. What can I do?
Please enable 'Modify default hard disk icons' on the Configuration, Disk Control panel. If you use Windows XP, you may need to upgrade to SP2 to view the disk status on icons.
I encountered problem with Hard Disk Sentinel. What can I do?
Please try to use the latest available version, especially if you just performed a complete (re)installation. If you use latest possible hardware (new hard disk, new SSD, recent RAID controller, recent USB adapter or similar hardware) then make sure to use the latest Hard Disk Sentinel version as some very new hardware may be only supported by that.
If your device seems not supported, try the latest possible beta version from the Download Hard Disk Sentinel page, as such versions have frequent updates for new devices / hardware.
Upon any questions, problems, the best is always to use Report menu -> Send test report to developer option. This way it is possible to check the current status and advise quickly.
No Performance information displayed. What is wrong?
Cmd Hard Drive Info

The performance information is based on the Performance Counter objects of Windows (2000/XP/2003/Vista) systems. Hard Disk Sentinel reads these counters and displays performance information based on them. Hard Disk Sentinel has no control on these counters, how they work because they are controlled by Windows itself.
The operating system assigns performance counters to hard disks while booting. So if the disk is an external one and connected later (after Windows completed the booting sequence), the performance monitoring may not be possible.
If the performance information is missing for ALL disks, then disk performance monitoring is globally disabled. Please click Start -> Run -> CMD.EXE (to open a console window) and type diskperf -y (ENTER). You may need to restart the computer to let Windows create the performance counter objects on startup.
If the above command does not help, please try the following:
Click Start -> Run -> Regedit
navigate to the following subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesPerfdiskPerformanceIf there is a value called Disable Performance Counters listed there, and it has a numerical value of one (1), just change it to zero (0), and reboot.
The full procedure is available at: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa998009.aspx
Fix performance counters under Win7 (thanks to Neolisk): Click Start, type cmd right click cmd.exe, and select Run as administrator.
At the prompt, type lodctr /r and press ENTER. This will repair the pointers (those are stored in the registry).
If it says (Disabled) next to a provider, you can enable it with lodctr /e:(provider name). Use for (provider name) the string between the [ ] at the beginning of the entry (more information at this page).
Fix performance counters under Windows 10 (thanks to Yannis): if you attempt to use lodctr /r and receive Error: Unable to rebuild performance counter setting from system backup store, error code is 2, then please try the following method (enter the commands marked with bold):
and then reboot the system to repair performance counters.
If the above does not work, you can manually try to verify if the operating system detects the performance values. To do this, please start the performance monitoring tool from Microsoft:
Click Start -> Run and type 'Perfmon'.
On the bottom right side of the window (under the graphs) you can see a list of currently displayed performance counters. Please click on them and press 'DEL' button to remove all.
Then above this space (on the empty graph) please right click and select 'Add Counters'
Under 'Performance Objects' please select 'PhysicalDisk'
Under 'Select counters from list' please select '% Disk Time' (or 'Disk Bytes/Sec' - these two counters are displayed in Hard Disk Sentinel).
Under 'Select instances from list' please select instances for your drives (eg. '0 C:') or select all.
Click on 'Add' and then 'Close'.
Now you should see how the values are changing for the selected hard disks. Please copy or move some files to see how the graphs are changing, reflecting the actual disk usage or the transfer rate. You can compare the values displayed here and in Hard Disk Sentinel. These should be nearly the same (some differences is possible because of the different sampling times).
Here are more details about re-building performance counter objects of Windows. In case of a trouble (no performance information displayed), please check the following pages:
How to manually rebuild Performance Counter Library values
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;300956&Product=winsvr2003
PerfMon Problems (Win7)
http://social.answers.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/w7performance/thread/e90f231d-0014-457d-8b1f-5f342971597a
Update: if you experience that the real time performance monitoring works but after some time (for example after connecting/removing external hard disk, pendrive or similar storage device) it stops working, it may be caused by a function which allows performance monitoring when a new device (for example external hard disk) is connected. When this happens, Hard Disk Sentinel clears the performance object cache and re-detects the performance objects. On some systems (regardless of hardware configuration) this function causes that Windows disable performance monitoring at all.
If this happens, you may try to disable this function this way:
1) click 'start' (Windows) button and to the search field enter REGEDIT
2) open REGEDIT
3) navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432NodeHD Sentinel
(or HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREHD Sentinel under 32 bit Windows)
4) create a new STRING key named DisablePerfCacheClear and specify value of 1 for that.
If this is configured and restart, Hard Disk Sentinel will not issue this special function to clear performance object cache when it detects the change of configuration so hopefully the counters will continue working.
I have bad sectors and my disk health is 90%. Do I need to worry or ask for replacement drive?
It is important to know that any small, microscopic scratch or dust can cause some bad sectors on the disk surface. It is hard to avoid all of these problems and it is possible that the drive is not 100% perfect, but the health is still 'excellent', so you do not need to worry about these sectors.
Especially, because these sectors are not used any more: the hard disk reallocated them and all read and write operations are redirected to the spare area instead.
The problem would start only when the number of these sectors increase (decreasing the health value of the disk).
Hard Disk Sentinel is the only software which is sensitive enough to detect the real number of problems and give textual description based on the real status of the hard disk.
The important thing is that it can detect any slight decrease in the health. For example, you can be alerted and can verify any (even very small) problems occurred with your hard disk - otherwise such problems may not be noticed, until the disk failure appears.
Please press F1 in the software to open the help and select 'Appendix -> Text description' for more information. You can find the same information at: https://www.hdsentinel.com/help/en
If you are interested, please check the article describing How Hard Disk S.M.A.R.T. Works?
You can read about the problems with original SMART feature of the disk drives, and a possible solution built into Hard Disk Sentinel. The example also shows the importance of being notified about all disk problems to prevent data loss and costly data recovery.
You should not ask your vendor for replacement drive in this situation. Hard disk manufacturers define different methods to verify when a hard disk should be replaced in terms of warranty: when they have 'enough' problems (not only bad sectors) to reach a specified threshold. At this time, the hard disk has usually serious problems and may be seriously damaged which prevents data recovery. At this time, Hard Disk Sentinel displays 0 % health. You can ask for replacement hard disk only when the hard disk health is 0 %.
Hard disk health is low or recently changed or I just installed a new (used) hard disk. How can I perform a deep analysis?
All problems found during the lifetime of hard disk are reported in the text description field for this hard disk. If the hard disk health is not 100% and the text description shows problems (for example 'bad sectors'), it is recommended to click on the '?' button next to this field as it describes the current situation and tell more information about what are the next steps. It is available online at https://www.hdsentinel.com/help/en/text_description.html
However, there may be even further problems which may not yet detected, for example on less frequently accessed surface areas. To reveal any problems (and correct them), it is recommended to use the hard disk tests available in Hard Disk Sentinel.
When the hard disk health changes, it is highly recommended an immediate backup of all stored data to an other hard disk prior any diagnostics.
In this situation, the most important is to verify if the hard disk status is stable (regardless of the health %) or if there are further problems which may not be revealed yet. This determines if the drive can still be used or if replace is required (warranty replacement is possible at 0% health, when the number of problems reach the threshold specified by the manufacturer).
Different hard disk tests are available in the Disk menu. First of all, try Disk -> short self test which generally checks hard disk components (heads, servo, internal memory, etc.). It may quickly report problem but it is possible that it completes without problems - as this test does not scan the entire hard disk surface. The next step is to use the Disk -> Extended Self-test option which is a hardware test with complete surface verification. If this completes without error, the hard disk surface seems to stable at the moment. However, if the health is less than 100%, it is expected that it will report an error at some point of the test and will stop.
If this happens, the Disk -> Surface Test option should be used. This contains different test steps which run in controlled and managed environment. For the first time, it is best to use the READ test. This may not fix possible issues but may reveal the amount and the seriousness of errors. If this completes without error (all data blocks will be green as on this image, then the disk already fixed all problems and it is safe to use it in the future.
However, if yellow and/or red spots (example image) or even larger areas (example image, example image) are affected, there are further problems expected which cause data loss.
These areas can only be analyzed and fixed by WRITE tests. The best method is to use the Disk -> Surface test -> Reinitialise disk surface which Overwrites the disk surface with special initialization pattern to restore the sectors to default (empty) status and reads back sector contents, to verify if they are accessible and consistent. Forces the analysis of any weak sectors and verifies any hidden problems and fixes them by reallocation of bad sectors (this is drive regeneration).
Because of its nature (overwrites all information) it cannot be used on primary (system) drive, only on secondary drive, for example on a drive used in external USB enclosure.
If you select Disk -> Surface test option, you can read the details of all such tests and how they affect stored data (read only or overwrite/delete all stored data).
To summarize, the following steps are the best to detect and repair hard disk problems:
1) Disk -> Short self test
2) Disk -> Extended self test
3) Disk -> Surface test -> Read test
4) Disk -> Surface test -> Reinitialize disk surface
Further tests are possible to verify disk stability, noise and temperature levels (Disk ->Random seek test) or Disk -> Surface test -> Refresh data area which is useful for other devices (for example SSDs and pendrives, memory cards) to prevent 'forget' effect of memory cells.
For more information, please check the Help -> Hard disk tests topic by F1 or online at https://www.hdsentinel.com/help/en, also in FAQ: https://www.hdsentinel.com/faq.php#health
Why other software displays different health? Which is correct?
Basically, as you may see, all software are based on the S.M.A.R.T. (self-monitoring) values reported by the drive.
These contain status information about different sensors built into the drive (both current values and ever measured).
Different software calculate health differently based on these attributes. Most software uses the relation between the 'value' and the 'threshold' fields for the attributes to measure how 'good' an attribute is (and shows a health value based on that).
Researches showed that this method is wrong. It is not able to show the real number of problems and not able to predict failures as in most cases, it displays far better status than should. (if you are interested in further details, please check How Hard Disk S.M.A.R.T. Works? and check the example at the bottom: the failed disk seemed perfect in other software).
This is why the development of Hard Disk Sentinel was started.
Personally I'd only trust a software which can tell (by the text description) what kind of problems found or why the health is 100%, 97%, 60% or so (what kind of problems found or not found).
For example, it is possible that an other software noticed some errors but not properly identified all issues. That may report 95-100% status - even for a drive which has lots of problems as reported in the text description of Hard Disk Sentinel.
Hard Disk Sentinel offers numerous test functions to verify if the disk status is stable and/or if there are any furhter problems with the drive. If the drive status is stable, you may continue using it - with constant monitoring and using a software which is sensitive enough to report any new (even minor) problems, allowing to perform a backup (it is even possible to configure Hard Disk Sentinel to perform automatic backup upon that).

Please check https://www.hdsentinel.com/faq.php#tests for more information about the recommended steps in this situation.
If you can use Report menu Send test report to developer option in Hard Disk Sentinel, I can check the complete status of the disk drive and may advise based on that.
I believe TRIM is enabled (fsutil shows that), but Hard Disk Sentinel shows it is DISABLED. Why?
There is a big difference between the TRIM feature being enabled and being active. Enabled just means that the OS will send the TRIM command to the SSD device (via the controller driver where the SSD is connected), but that does not guarantee that the SSD will actually receive the TRIM command.
The fsutil shows if the operating system in general uses the TRIM function or not.
The result of this is completely useless - as it returns 0 (TRIM 'working') even if there is no SSD present in the system.
If the result is 0, it means that the operating system is prepared to send the TRIM command for the proper device (an SSD with TRIM function supported).
The question is: does the hard disk controller (and its driver) pass this command to the SSD(s) used in the system or block it?
The problem is that some hard disk controllers (and their drivers) may block the TRIM command, do not pass it to the SSD, even if TRIM is supported by the SSD. (this is same as the 'Acoustic management' command for hard disks may be blocked when using some disk controllers).
For example, if you'd have two or more SSDs (supporting TRIM) in your system, it may be possible that TRIM may be transferred properly to one of them - but not for the other(s) if the SSDs are connected to different hard disk controllers.
Hard Disk Sentinel checks the real usage of TRIM for each appropriate device (one-by-one). If it displays 'disabled', it means there is a problem with the driver of the hard disk controller (if both the OS and SSD should support TRIM). Usually updating this driver from the Driver Zone may help. If not, using a different hard disk controller may also helpful.
The issue is very common with Marvell 91xx controllers. Because the driver of these Marvell controllers has several problems, it may be better to replace it with Windows 'Standard AHCI Controller' in the following way:
- open Windows Device Manager and locate the Marvell 91xx SATA 6G Controller (AHCI).
- try the update driver option and select to use 'Standard AHCI Controller' driver for the controller.
After this change and restart of the system, TRIM will be really working and reported by Hard Disk Sentinel.
If you prefer, please use Report -> Send test report to developer option so I can check the disk controller and may advise on the proper driver used.
-->This article provides solutions to an issue where you fail to select or format a hard disk partition when you try to install Windows.
Original product version: Windows 7 Service Pack 1, Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 927520
Note
Support for Windows Vista without any service packs installed ended on April 13, 2010. To continue receiving security updates for Windows, make sure you're running Windows Vista with Service Pack 2 (SP2). For more information, see Support is ending for some versions of Windows.
Important
Dynamic discs are only supported for:
- Windows Vista Business
- Windows Vista Enterprise
- Windows Vista Ultimate.
- Windows 7 Enterprise
- Windows 7 Professional
- Windows 7 Ultimate
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard
- Windows Web Server 2008 R2
They are not supported for Windows Vista Home Basic, Windows Vista Home Premium, Windows 7 Home Basic, Windows 7 Starter, and Windows 7 Home Premium.
There is one exception. When you upgrade your computer from Windows XP Media Center Edition to Windows Vista Home Premium, some dynamic discs are handled and supported.
Symptoms
When you try to install Windows Vista, Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, you may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
The hard disk on which you want to install Windows Vista, Windows 7, or Windows Server 2008 R2is not listed.
You cannot select a hard disk partition on which to install Windows Vista, Windows 7, or Windows Server 2008 R2.
You cannot format a hard disk partition or partitions.
You cannot set the correct size for a hard disk partition.
You receive the following error message:
Windows is unable to find a system volume that meets its criteria for installation
Cause
This problem may occur for one of the following reasons:
- Windows is incompatible with a mass storage controller or a mass storage driver.
- A mass storage controller or a mass storage driver is outdated.
- The hard disk on which you want to install Windows Vista, Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 is a dynamic disk.
- A data cable in the computer is loose, or another hardware issue has occurred.
- The hard disk or the Windows file system is damaged.
- You tried to select a FAT32 partition or another type of partition that is incompatible with Windows Vista, Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2.
To resolve this problem, use one or more of the following methods.
Resolution 1: Verify that partition is compatible with Windows
You cannot install Windows on a FAT32 partition. Additionally, you must correctly configure dynamic disks for use with Windows. To verify that the partition is compatible with Windows Vista, Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, follow these steps:
For a dynamic disk that has a simple volume, use the Diskpart.exe utility to configure the disk as an active disk. For more information about how to use the Diskpart.exe utility, see DiskPart Command-Line Options.
For a FAT32 partition, reformat the partition, or convert the partition to an NTFS file system partition by using the Convert.exe command.
Note
When you format a partition, all data is removed from the partition. This data includes all the files on the partition.
Resolution 2: Update drivers for the hard disk controller
If you want to install Windows Vista Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 as an upgrade, update the drivers for the hard disk controller to the latest drivers.
Note
Windows Setup provides a feature to migrate current drivers to the new operating system. Therefore, Windows Setup may use the drivers that are currently installed on the computer. If the computer does not have the latest drivers installed, the Setup program may use the outdated drivers. In this case, you may experience compatibility problems.
Resolution 3: Provide correct drivers for hard disk controller
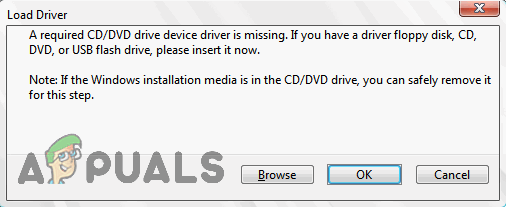
If you are trying to perform a clean installation of Windows, you must provide the correct drivers for the hard disk controller. When you are prompted to select the disk on which to install Windows, you must also click to select the Load Driver option. Windows Setup will guide you through the rest of the process.
Resolution 4: Examine Setupact.log file to verify that partition is active
If you receive the following error message, verify that the partition is active by examining the Setupact.log file:
Windows is unable to find a system volume that meets its criteria for installation
Note
- If you install Windows Vista, Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 as an upgrade, the Setupact.log file is located in the Drive:$WINDOWS.~BTSourcesPanther folder. Drive represents the drive that contains the existing Windows installation.
- If you perform a clean installation of Windows Vista, Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, the Setupact.log file is located in the Drive:$WINDOWSSourcesPanther folder. Drive represents the DVD drive that contains the Windows Setup files.
To verify that the partition is active, follow these steps:
Insert the DVD into the DVD drive.
On the disk selection screen, press SHIFT+F10. A Command Prompt (CMD) window opens.
Change the directory to locate the Setupact.log file, and then open the Setupact.log file.
Locate the DumpDiskInformation section. This section contains information about partition mapping.
In the DumpDiskInformation section, locate the log entry that resembles the following.
Disk [0] partition [1] is an active partition
If this log entry appears after an entry that resembles the following, the hard disk may not be configured to use a Windows-based operating system.
Unknown
In this case, use the Diskpart.exe utility to configure a different partition as active.
Note
This step prevents a third-party operating system from starting.
Close the Command Prompt window.
Resolution 5: Check for firmware updates and for system BIOS updates
For firmware updates and for system BIOS updates, contact the manufacturer of the hardware in the computer.
Resolution 6: Verify that system BIOS correctly detects hard disk
For information about how to verify that the system BIOS correctly detects the hard disk, contact the manufacturer of the computer hardware.
Resolution 7: Use Chkdsk.exe to check for problems
Run the Chkdsk.exe utility to check for disk problems. Replace the hard disk if it is damaged.
Resolution 8: Use Diskpart.exe to clean disk and rerun Windows Setup
If you have tried all the methods that are listed in this section and the problem persists, use the Diskpart.exe utility to clean the disk, and then run Windows Setup again.
Note
Use this method only if you want to perform a clean installation of Windows. When you clean the hard disk, it is formatted. All partitions and all data on the hard disk are permanently removed. We strongly recommend that you back up the files on the hard disk before you clean the disk.
Scan Disk Cmd
To use the Diskpart.exe utility to clean the hard disk, follow these steps:
Cmd Disk Repair
- Insert the DVD into the DVD drive.
- On the disk selection screen, press SHIFT+F10. A Command Prompt window opens.
- Type diskpart, and then press ENTER to open the diskpart tool.
- Type
list disk, and then press ENTER. A list of available hard disks is displayed. - Type
sel disk number, and then press ENTER. number is the number of the hard disk that you want to clean. The hard disk is now selected. - Type
det disk, and then press ENTER. A list of partitions on the hard disk is displayed. Use this information to verify that the correct disk is selected. - Make sure that the disk does not contain required data, type
clean all, and then press ENTER to clean the disk. All the partitions and all the data on the disk is permanently removed. - Type
exit, and then press ENTER to close the diskpart tool. - Close the Command Prompt window.
- Click the Refresh button to update the disk selection screen. This step lists the disk.
- Run Windows Setup to perform a clean installation of Windows.

Comments are closed.